Architecture Overview¶
Single Source of Truth¶
The OVES Access Management system serves as the authoritative single source of truth for all identity, access control, and security policies across the organization. This centralized approach ensures:
- Unified Security Posture: All access decisions flow through this system
- Consistent Policy Enforcement: No shadow IT or bypassed authentication
- Complete Audit Trail: Every access event is logged and traceable
- Centralized Control: Business owners maintain ultimate authority over all access
Continuity-First Design¶
The architecture is specifically designed to maintain security continuity as personnel change:
Personnel Rotation Resilience¶
- Role-Based Architecture: Access tied to business roles, not individuals
- Documented Processes: All configurations and procedures are documented
- Automated Provisioning: Reduces dependency on individual knowledge
- Emergency Access Procedures: Business owners can always regain control
Business Owner Authority¶
- Ultimate Control: Business owners retain final authority over all access policies
- Override Capabilities: Emergency access procedures bypass technical dependencies
- Approval Workflows: Critical changes require business owner authorization
- Audit Oversight: Business owners have visibility into all access activities
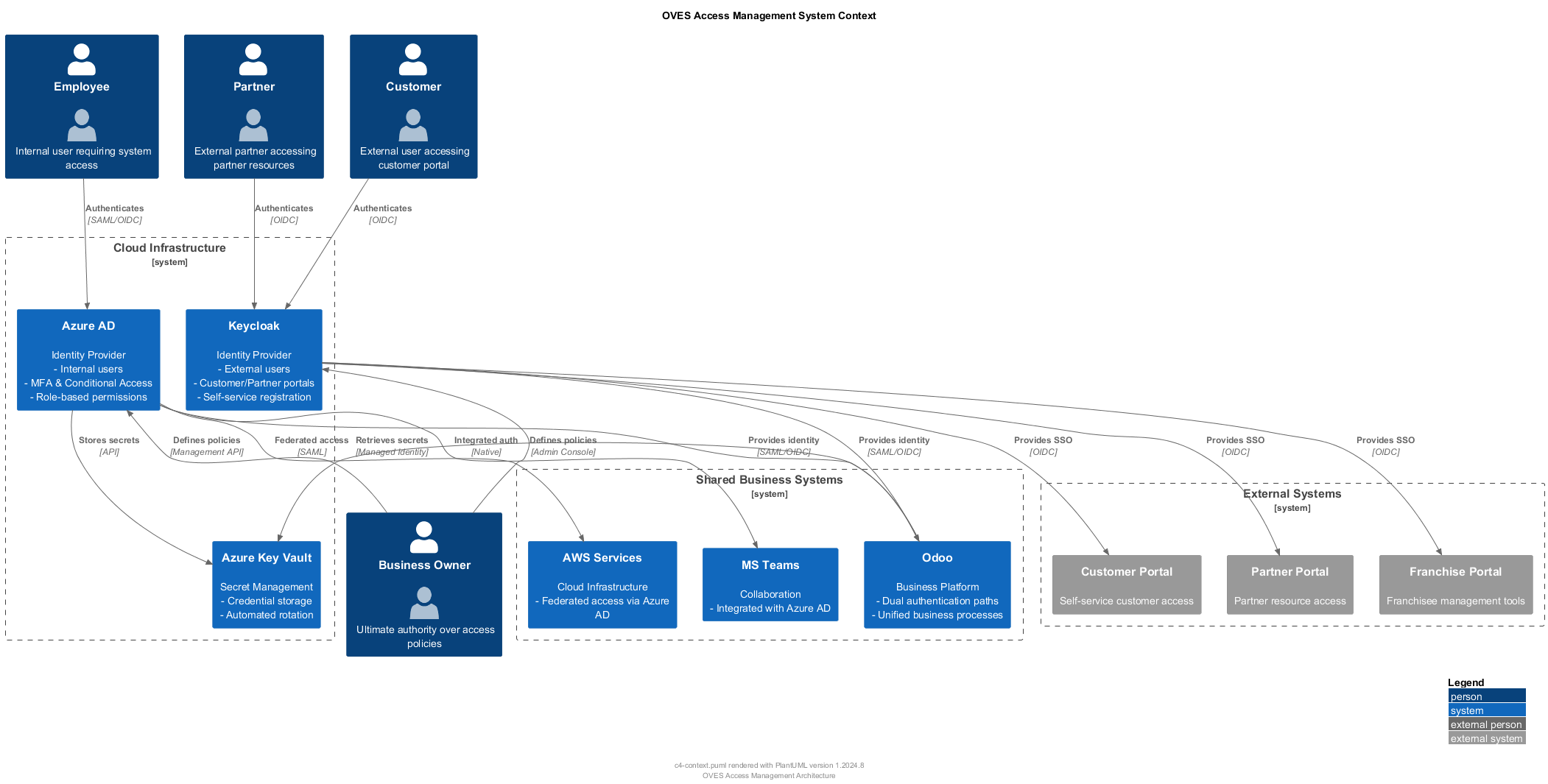
System Architecture Context¶
The OVES Access Management system serves as the authoritative single source of truth for all identity, access control, and security policies across the organization. This C4 Context diagram shows the high-level system boundaries and key stakeholders:
Click diagram to view PlantUML source
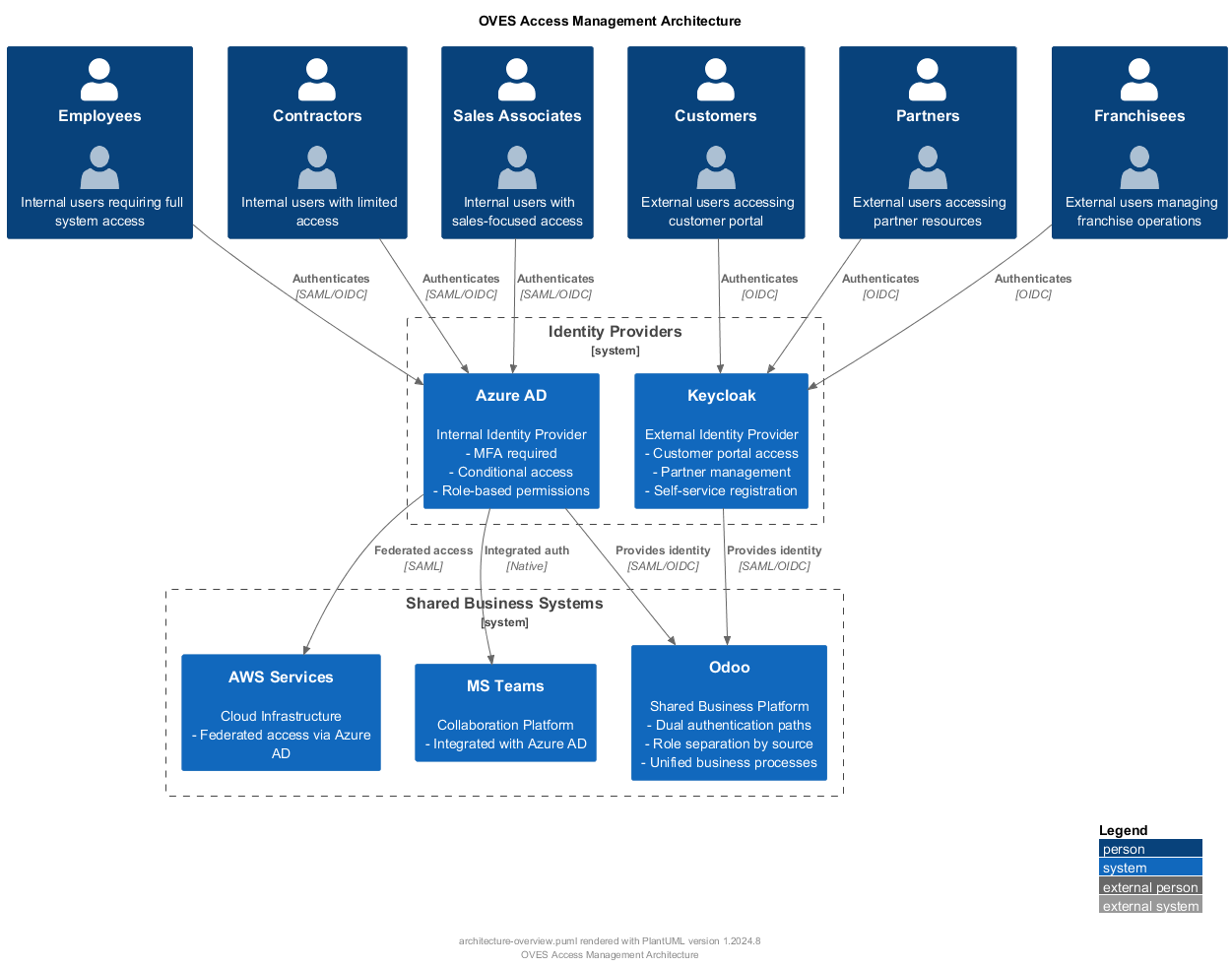
Detailed System Architecture¶
The system is built on a dual identity provider architecture that cleanly separates internal and external user management while providing seamless integration through shared resources:
Click diagram to view PlantUML source
Core Components¶
1. Azure AD (Internal Identity Provider)¶
Purpose: Manages all internal user identities and access control
Features: - Multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Conditional access policies - Role-based access control (RBAC) - Centralized secret management
Managed Users: - Employees (full access) - Contractors (limited access) - Sales associates (sales-focused access)
2. Keycloak (External Identity Provider)¶
Purpose: Manages external user identities and customer-facing services
Features: - Single sign-on (SSO) for customer portal - Customer data privacy compliance - Partner and franchisee management - External service integration
Managed Users: - Customers (subscription access) - Partners (partner portal) - Franchisees (franchise management)
3. Odoo (Shared Business Platform)¶
Purpose: Central business platform with dual authentication
Features: - Dual-path authentication (Azure AD + Keycloak) - Role separation by identity source - Integrated business processes - Unified data management
Governance and Control Structure¶
Business Owner Authority Matrix¶
| Control Level | Business Owner | IT Administrators | Developers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy Creation | ✅ Ultimate Authority | 🔧 Implementation | ❌ No Access |
| Access Approval | ✅ Final Decision | 📋 Recommendation | ❌ Request Only |
| Emergency Override | ✅ Full Control | ⚠️ Limited Scope | ❌ No Access |
| Audit Review | ✅ Full Visibility | 📊 Technical Logs | ❌ Limited View |
| System Configuration | ✅ Approval Required | 🔧 Technical Implementation | 🛠️ Development Only |
Continuity Safeguards¶
- Documentation Standard: All procedures documented in this system
- Cross-Training Requirements: Multiple personnel trained on each component
- Emergency Procedures: Business owner bypass mechanisms always available
- Regular Reviews: Quarterly access reviews with business owner approval
- Knowledge Transfer: Structured handover processes for role transitions
Access Control Matrix¶
| Resource | Employees | Contractors | Sales | Customers | Partners | Franchisees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Odoo | ✅ Full | ✅ Limited | ✅ Sales | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Customer Portal | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Read | ✅ Full | ❌ | ❌ |
| Partner Portal | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Read | ❌ | ✅ Full | ❌ |
| Franchise Portal | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Read | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Full |
| AWS Console | ✅ Role-based | ✅ Limited | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| MS Teams | ✅ Full | ✅ Limited | ✅ Sales | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Security Architecture¶
Single Source of Truth Enforcement¶
All access decisions must flow through this system - no exceptions:
- No Direct Database Access: All data access requires authentication through identity providers
- No Bypass Mechanisms: All applications must integrate with the identity system
- Centralized Policy Engine: All access rules defined and enforced centrally
- Unified Audit Trail: Every access attempt logged regardless of source system
Defense in Depth¶
- Network Layer: VPN and network segmentation
- Identity Layer: Strong authentication with MFA
- Application Layer: Role-based access controls
- Data Layer: Encryption at rest and in transit
- Monitoring Layer: Comprehensive audit logging
Secret Management Strategy¶
| Secret Type | Storage Location | Access Method | Rotation Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal APIs | Azure Key Vault | Azure AD Service Principal | 90 days |
| Customer APIs | Keycloak Vault | Keycloak Client Credentials | 90 days |
| Database | Azure Key Vault | Managed Identity | 180 days |
| Third-party | Azure Key Vault | Azure AD App Registration | 60 days |
Integration Patterns¶
1. Federated Identity¶
Both Azure AD and Keycloak integrate with Odoo using federated identity protocols:
- SAML 2.0 for enterprise SSO
- OpenID Connect for modern applications
- OAuth 2.0 for API access
2. Role Mapping¶
Identity provider roles are mapped to Odoo permissions:
Azure AD Roles → Odoo Groups:
"OVES-Employees" → "Internal Users"
"OVES-Sales" → "Sales Team"
"OVES-Contractors" → "Limited Users"
Keycloak Roles → Odoo Groups:
"Customer" → "Portal Users"
"Partner" → "Partner Users"
"Franchisee" → "Franchise Users"
3. Data Separation¶
- Internal Data: Managed by Azure AD permissions
- Customer Data: Managed by Keycloak permissions
- Shared Data: Accessible based on source identity provider
Compliance and Auditing¶
Audit Trail Components¶
- Azure AD Logs: Internal user activity
- Keycloak Logs: External user activity
- Odoo Logs: Business process activity
- AWS CloudTrail: Infrastructure activity
Compliance Standards¶
- SOC 2 Type II: Security and availability controls
- GDPR: Customer data protection (Keycloak managed)
- ISO 27001: Information security management
- NIST Framework: Cybersecurity standards
Personnel Transition Procedures¶
Developer/Administrator Rotation¶
The system continues operating securely regardless of personnel changes:
- Immediate Access Revocation: Automated deprovisioning when personnel leave
- Knowledge Transfer Protocol:
- All configurations documented in this system
- Handover checklists for each role
- Shadow period with overlapping access
- Emergency Continuity:
- Business owner maintains master access
- Break-glass procedures documented
- External contractor access available
- Skills Transfer:
- Cross-training requirements for critical systems
- Documentation-first approach to all changes
- Vendor support relationships maintained
Business Owner Continuity¶
- Succession Planning: Clear business owner succession documented
- Delegate Authority: Temporary delegation mechanisms available
- Recovery Procedures: Business owner can always regain full control
- Legal Framework: Authority tied to business roles, not individuals
Scalability Considerations¶
Performance Optimization¶
- Identity Provider Clustering: High availability for both Azure AD and Keycloak
- Database Optimization: Separate read/write replicas for Odoo
- Caching Strategy: Redis for session and authentication caching
- CDN Integration: Global content delivery for customer portals
Growth Planning¶
- User Scaling: Support for 10,000+ internal and 100,000+ external users
- Geographic Distribution: Multi-region deployment capability
- Service Isolation: Microservices architecture for independent scaling
- API Rate Limiting: Prevent abuse and ensure fair usage
Next: Learn about specific Identity Provider configurations or jump to Azure AD Implementation.